The term ‘Homicide’ is derived from Latin word ‘homi’ which refers Man and ‘Cido’ which means killing (cut). Therefore it means ‘causing another person’s death’.Homicide simply means the killing of a person. Homicide is when one person causes the death of another person, intentionally or unintentionally. Killing humans against the Fundamental rights and human rights. It violates a person’s right to life and liberty.
Homicide would be categorized into two types, which are mentioned below:
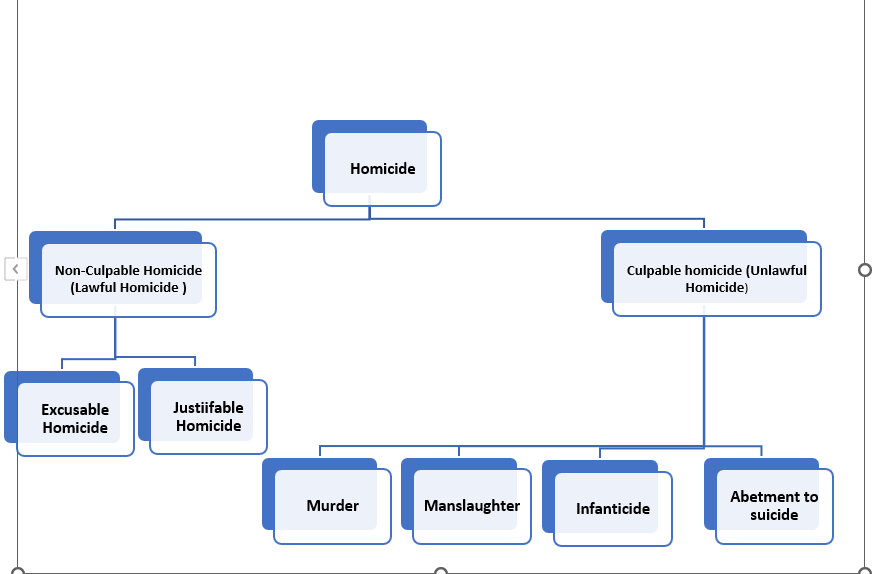
1. Non- Culpable Homicide (Lawful Homicide)
Non- Culpable Homicide refers to the killing of a person that is not considered a crime under criminal law. This type of Homicide is typically not punishable because the person responsible for the death did not act with intention, recklessness or negligence.
Non-Culpable Homicide is also Divided into Excusable homicide and Justifiable Homicide.
A. Excusable Homicide
It refers to a killing that occurs by accident or in situations where the person committing the act had no intention to cause harm and acted without negligence. It typically arises under circumstances where the law recognizes that the individual was not entirely at fault due to misfortune or lack of intent. The types of excusable homicide are mentioned below:
(i) Infancy: Infancy refers to the legal principle that children below a certain age lack the mental capacity to form the necessary intent(Mens rea) to commit a crime, Therefore, a homicide committed by a child below the specified age is considered excusable homicide.
In the context of Nepal, According to Section 13 of the Muluki Penal Code, 2074, an Act of a child is not an offence. This section states, “No Act done by a child below ten years of age shall be Considered to be an offence.
(ii) Insanity: When a Person is found to be legally insane at the time of committing a homicide, they may not be held criminally responsible because they lack the mental capacity to understand the nature or wrongfulness. Therefore, a Homicide committed by an insane person falls under excusable homicide.
In the context of Nepal, According to Section 14 of the Muluki Penal code,2074 ” Act done by a person of unsound mind not to be offence.”
(iii) Intoxication: Intoxication refers to a state in which a Person’s normal Physical and mental faculties are impaired due to the consumption of substances such as alcohol, drugs, or other intoxicants. So, In homicide, refers to a situation where a person commits a homicide while under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Therefore a homicide committed by an intoxicated person is considered excusable homicide.
(iv) Mistake: A mistake is a misunderstanding or erroneous belief regarding a fact or law at the time an act is committed.In criminal law, if someone makes a reasonable and genuine mistake, it can prevent them from having criminal intent (mens rea) and may excuse them from being held responsible for the crime.
Mistake are classified into 2 types :
1. Mistake of Law: A wrong understanding of the law, which usually does not excuse someone because “ignorance of the law is no excuse.”
2. Mistake of Fact: A wrong belief about something factual, which might excuse a person if it was genuine and reasonable.
In the context of Nepal, According to section 8 of the Muluki Penal Code,2074 “Act done by mistake of fact not to be offense”. Therefore, a homicide committed in mistake of fact may not be treated as a criminal act, and in some cases, it could be considered excusable homicide.
B. Justifiable Homicide
A justifiable homicide is a homicide that is commanded or authorized by law. In other word , justifiable homicide is when an individual kills another on purpose but for a valid, lawful reason. A death can be deemed a justifiable homicide if it was done to protect oneself, others or one’s property from serious harm or death and was devoid of criminal intent or motive.
Types of Justifiable homicide include:
(i). Necessity: The act is done without any criminal intention to cause harm and in good faith for the purpose of preventing or avoiding other harm to person or property is known as Principle of Necessity. therefore , A Homicide committed out of Necessity is considered Justifiable homicide.
According to Section 23 of the national penal code,2074: “Act done in good faith to prevent other harm not to be offence”.
(ii). Duress: Duress is a threat or force meant to make someone to do something. Therefore, a homicide committed under duress, where the individual acts to protect themselves or others from an imminent and serious threat, is considered a justifiable homicide.”
In the context of Nepal, according to Section 22 of the National Penal Code, 2074: ‘An act done, compelled by fear or threat, shall not be considered an offense.’ However, this does not apply in cases of homicide in Nepal, although some countries still recognize it as justifiable homicide.”
(iii). Death Penalty: It is also known as capital Punishment. It is a legal process in which a person is sentenced to death by the state as a punishment for committing certain crimes, Typically those Considered the most serious Crimes, Such as Murder, Treason, or terrorism.
(iv). Self Defence: The use of reasonable force to protect oneself or members of the family or properly from bodily harm from the attack of an aggressor.If the defender has reason to believe that they are in danger, is considered self defence.Therefore, a homicide committed in self-defense is considered justifiable homicide.
In the context of Nepal, National Penal Code,2074 sections 24,25 and 26 has mentioned about to Self-defense.
(v). Protection of Chastity: It refers to effort to safeguard the sexual honor or purity of an Individual. Therefore, if a woman had committed a homicide while protecting her chastity, it can be considered as justifiable homicide.
In the context of Nepal, According to National Penal code 2074, Section 26,(2b), if there is cause the death of person, where an act is instantly done by the victim having reasonable cause to believe that the assault is made with the intention committing rape or at the time of or after the commission of rape is not Considered to be an offence.
(vi). Protection of Property: It refers to the use of reasonable force to prevent the unlawful destruction, theft, or intrusion upon one’s property. Therefore, if a homicide is committed in the process of protecting property from a serious threat, it can be considered justifiable homicide.
In the context of Nepal, according to section 24(2) of the National Penal Code 2074: “Every person has a right to defend the body, life or
property of his or her own or of any other person against any illegal harm.”
(vii). Superior Order: This refers to the instruction given by the higher authority, such as the Commanding officer or superior which a person might follow even if those orders involve committing homicide. Such Homicide can be considered justifiable homicide.
2. Culpable Homicide (Unlawful Homicide)
The act of causing the death of another person with intent, knowledge, or recklessness is known as culpable Homicide.
According to Section 299 of IPC “ Whoever cause death by doing an act with the intention of causing death,or with the intention of causing such bodily injury as is likely to cause death, or with the knowledge that he is likely by such act to cause death,Commits the offence of culpable Homicide.
Culpable Homicide can be categorized into 4 types :
(A) Murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of any person with the intention to kill or to cause grievous bodily harm to that person. Every Murder is a culpable homicide, but every homicide is not murder. It is the most heinous form of killing.
it can be divided into different types as per the National Penal code ,2074 which are mentioned below :
(i) Intentional Killing : According to Section 177 of National Penal Code, 2074 “No person shall Intentionally kill, or do ,or cause to be done, any act causing the death of another person.” A person who commits or causes such an offence, shall be liable to the sentence of life Imprisonment.”
(ii) With knowledge of the act that causes death: According to section 178 of National Penal Code 2074, “No Person shall do any act, with the knowledge that, or having reason to believe that such act is, in an ordinary cause, likely to cause the death of another person.” If death results from such an act, the offender will be liable to life imprisonment.
(iii) Transferred of malice: It refers to an act of killing a person not intended to be killed. According to Section 180 of the National Penal Code,2074,”Where a Person by doing anything which he or she intends to cause or knows to be likely to cause or has reasons to believe to be likely to cause death of anyone other than the one whose death was so intended is known as transferred of malice.” and S/he shall be liable for sentence according to section 177,178 and 179.
(B) Manslaughter
Manslaughter means unlawful killing of another person without malice aforethought. This means that the killing was intentional but not Premediated or Planned. There are two types of Manslaughter .
(i) Voluntary Manslaughter: This occurs when a person kills another in the heat of passion or as a result of sudden provocation. This Killing must be a direct result of the Provocation and not a result of a plan or cooling period.
According to section 179 of National Penal Code 2074 there is a Provision regarding the “Prohibition of causing death by grave provocation or in heat of passion”. Where mentioned that ” a person who causes death under certain circumstances, such as grave provocation, excess use of self-defense, or in the heat of passion, may be sentenced to 10 to 15 years of imprisonment and fined 100,000 to 150,000 rupees. However, this does not apply in cases of premeditated murder or deliberate afterthought.”
(ii) Involuntary Manslaughter: Involuntary manslaughter is defined as an individual who has committed an unlawful killing without an intention to cause grievous bodily harm or kill the victim, causing the death by recklessness or gross negligence instead. It refers to when a person kills another person through reckless or negligent behavior.
According to Section 181 of National Penal Code 2074 there is a provision regarding the ” Prohibition of causing death by recklessness”. It is mentioned that ” No person shall cause the death of anyone by doing a reckless act. If a person cause the death of another person by recklessness act shall be liable to a sentence of imprisonment for a term of three to ten years and a fine of thirty thousand to one hundred thousand rupees.
According to Section 182 of National Penal Code 2074 there is a provision regarding the “Prohibition of causing death by negligence” Where mentioned that” No person shall causes the death of another person by doing a negligent act, except in the case of causing death due to grave provocation or in heat of passion. If a person cause the death of anyone one by negligence act, They shall be liable to a sentence of imprisonment for a term not exceeding three years and a fine not exceeding thirty thousand rupees.
(C) Infanticide
Infanticide is an act of intentionally killing a newborn baby or very young child. it refers to causing the death of an infant.
According to Section 184 of the National Penal Code 2074, there is a provision regarding the “Prohibition of throwing or abandoning Person under one’s own
guardianship” which state that ” A Person being bound to care or maintain an infant, child, disabled patient or elderly person, shall not so throw,
abandon or desert them in a manner that causes danger to the body or life of such infant, child, patient or elderly person. If such act causes the death of such child, disabled patient or elderly person. In that case, the offender shall be liable to a sentence of imprisonment for a term not exceeding seven years and a fine not exceeding seventy thousand rupees. Provided that if the throwing, abandonment or neglect causes the death of an infant, the offender shall be liable to life imprisonment.
(D) Abetment of Suicide
It is a Criminal Offense that occurs when a person encourages assists, or aids another person in committing suicide. This can include providing the means for suicide, such as a weapon or poison, or offering words of encouragement or persuasion.
According to Section 185 of National Penal Code 2074, there is a provision regarding the “Prohibition of Abetment of Suicide” which states that ” No person shall abet the commission of suicide by another, or create, or cause to be created, such circumstances as likely to lead towards the commission of such act.” If a person commits the offense or such act(abet)which leads towards the commission of suicide shall be liable to a sentence of imprisonment for a term not exceeding five years and a fine not exceeding fifty thousand rupees.




